Caution: With tools such as these, we do not condone their use for anything but testing networks for which you have the authority and for implementing defensive measures. Have fun!
Rainbow tables reduce the difficulty in brute force cracking a single password by creating a large pre-generated data set of hashes from nearly every possible password. Rainbow Tables and RainbowCrack come from the work and subsequent paper by Philippe Oechslin [1]. The method, known as the Faster Time-Memory Trade-Off Technique, is based on research by Martin Hellman & Ronald Rivest done in the early 1980’s on the performance trade-offs between processing time and the memory needed for cryptanalysis. In his paper published in 2003, Oechslin refined the techniques and showed that the attack could reduce the time to attack 99.9% of Microsoft’s LAN Manager passwords (alpha characters only) to 13.6 seconds from 101 seconds. Further algorithm refinements also reduced the number of false positives produced by the system.
The main benefit of Rainbow Tables is that while the actual creation of the rainbow tables takes much more time than cracking a single hash, after they are generated you can use the tables over and over again. Additionally, once you have generated the Rainbow Tables, RainbowCrack is faster than brute force attacks and needs less memory than full dictionary attacks.
Rainbow Tables are popular with a particularly weak password algorithm known as Microsoft LM hash. LM stands for LAN Manager, this password algorithm was used in earlier days of Windows and still lives on only for compatibility reasons. By default Windows XP or even Windows Server 2003 keeps the LM hash of your passwords in addition to a more secure hash (NTLM or NTLMv2). This allows for the benefit of backwards compatibility with older operating systems on your network but unfortunately makes the job of password cracking easier if you can obtain the LM hashes instead of the NTLM hashes.
Microsoft’s LAN Manager algorithm and its weaknesses
So why is the LM algorithm weak? “The LANManger scheme has several weaknesses, including converting all characters to uppercase, splitting passwords into 7-byte chunks, and not using an additional random element known as ’salt.” [2]
These three issues give rainbow tables their cracking power. By converting all characters to uppercase you effectively cut your key space in half. So if you had passwords of only characters (A-Z, a-z) you would think you would have 52 possibilities, but in reality with LM, you only have 26 because password are converted to all uppercase. So my way secure password of PaSsWoRd would be converted automatically to PASSWORD.
Passwords longer than 7 characters are split into 2 chunks so a 14 character password is effectively turned into two, seven character passwords (and converted to uppercase). The chunks can also be attacked separately as you will see when we start cracking passwords.
Lastly, by not salting any of the passwords no extra complexity is added to stored passwords.
For some more background info check out the LM section of Wikipedia.org: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LM_hash
From the Rainbow Tables wiki:
“Rainbow tables use a refined algorithm by using a number of different reduction functions to create multiple parallel chains within a single “rainbow” table, reducing the probability of false positives from accidental chain collisions, and thus increasing the probability of a correct password crack. As well as increasing the probability of a correct crack for a given table size, the use of multiple reduction functions also greatly increases the speed of lookups.
Rainbow tables are specific to the hash function they were created for e.g., MD5 tables can crack only MD5 hashes. The theory of this technique was first pioneered by Philippe Oechslin [3] as a fast form of time-memory tradeoff [4], which he implemented in the Windows password cracker Ophcrack. The more powerful RainbowCrack program was later developed that can generate and use rainbow tables for a variety of character sets and hashing algorithms, including LM hash, MD5, SHA1, and NTLM.”[5]
Let’s check out some sample rainbow table configurations and see how they fare, as we go thru the tutorial all of this should make more sense.
LM configuration #0
charset
|
[ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ]
|
keyspace
|
8353082582
|
table size
|
610 MB
|
success probability
|
0.9990
|
Has a success probability of 99.90% and only takes up 610 MB.
LM configuration #1
charset
|
[ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789]
|
keyspace
|
80603140212
|
table size
|
3 GB
|
success probability
|
0.9904
|
Has a success probability of 99.04% and takes up 3 GB.
LM configuration #5
charset
|
[ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789!@#$%^&*()-_+= ]
|
keyspace
|
915358891407 (2^39.7)
|
table size
|
24 GB
|
success probability
|
0.99909
|
Has a success probability of 99.1% and takes up 24 GB. This is starting to get large but 1) not THAT large with as cheap as hard drive space is and 2) with the character set involved. Don’t forget this will work on passwords up to 14 characters as well. What starts to make a difference is how long it takes to compute these tables.
LM configuration #6
charset
|
[ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789!@#$%^&*()-_+=~`[]{}|\:;”‘<>,.?/ ]
|
keyspace
|
7555858447479 (2^42.8)
|
table size
|
64 GB
|
success probability
|
0.999
|
Has a success probability of 99.9% and takes up 64 GB. This character set includes all possible characters on a standard keyboard (not including alt+xxx characters). So this table set is likely to crack any windows password up 14 characters in minutes. This is great but on one computer it will take about 2 years to generate these tables (Faster Time-Memory Trade-Off Technique).
You can see demos of some of these configurations in action at the Project RainbowCrack website [6].
Using Rainbow Tables & RainbowCrack
Example 1:
First download RainbowCrack for your platform from www.antsight.com/zsl/rainbowcrack/ .
We will use our LM alpha (configuration 0) rainbow tables.
** You will need to either create them or unzip [7] them and they the will look something like:
128,000,000 bytes lm_alpha#1-7_0_2100×8000000_all.rt
128,000,000 bytes lm_alpha#1-7_1_2100×8000000_all.rt
128,000,000 bytes lm_alpha#1-7_2_2100×8000000_all.rt
128,000,000 bytes lm_alpha#1-7_3_2100×8000000_all.rt
128,000,000 bytes lm_alpha#1-7_4_2100×8000000_all.rt
If everything goes well, backup all files (recommended especially if you just made them and didn’t download them) and then get ready to sort them.
To speed up the search of our rainbow table, we should sort the rainbow table with “rtsort.exe” in advance.
In fact “rcrack.exe” only accepts sorted rainbow tables.
We sort the rainbow tables by using the following command:
Use these commands:
rtsort lm_alpha#1-7_0_2100×8000000_all.rt
rtsort lm_alpha#1-7_1_2100×8000000_all.rt
rtsort lm_alpha#1-7_2_2100×8000000_all.rt
rtsort lm_alpha#1-7_3_2100×8000000_all.rt
rtsort lm_alpha#1-7_4_2100×8000000_all.rt
Each command will take several minutes to complete. The “rtsort.exe” utility will sort the file and write back to the original file.
Notice: If free memory size is smaller than the file size, we can’t load the file into memory at a time. In which case extra free disk space as large as the file to be sorted is required to apply an external sort.
Once rtsort has completed you are ready to use rcrack against some hashes.
To see available options just type “rcrack”
C:\rainbowcrack-1.2-win\rainbowcrack-1.2-win>rcrack
RainbowCrack 1.2 – Making a Faster Cryptanalytic Time-Memory Trade-Off
by Zhu Shuanglei < shuanglei@hotmail.comThis e-mail address is being protected from spam bots, you need JavaScript enabled to view it >
http://www.antsight.com/zsl/rainbowcrack/
usage: rcrack rainbow_table_pathname -h hash
rcrack rainbow_table_pathname -l hash_list_file
rcrack rainbow_table_pathname -f pwdump_file
rainbow_table_pathname: pathname of the rainbow table(s), wildchar(*, ?) supported
-h hash: use raw hash as input
-l hash_list_file: use hash list file as input, each hash in a line
-f pwdump_file: use pwdump file as input, this will handle LAN Manager ha
sh only
example: rcrack *.rt -h 5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592
rcrack *.rt -l hash.txt
rcrack *.rt -f hash.txt
Launch the program by issuing the command:
rcrack c:\rainbowcrack\*.rt -l hashlist.txt
You should replace “c:\rainbowcrack\” with where you placed your sorted rainbow tables.
To crack some hashed windows passwords, the syntax is similar:
rcrack c:\rainbowcrack\*.rt -f pwdumpfile.txt
rcrack c:\rainbowcrack\*.rt -l justhashlist.txt
rcrack c:\rainbowcrack\*.rt –h 213D466DB5B288F0F82E44EC0938F4F4
Where pwdumpfile.txt is the results of using a hash dumping utility like pwdump2, pwdump3, samdump, etc to dump the LAN Manager’s passwords.
If your password consists of only letters only, rcrack should be able to crack it with a success rate of 99.9%.
Let’s try it against the following hash file in pwdump format (so use the –f option):
remote:”":E52CAC67419A9A224A3B108F3FA6CB6D:8846F7EAEE8FB117AD06BDD830B7586C:::
randy:”":98B5AFEB67293D6AAAD3B435B51404EE:A9F34664151F6360757B31644F37E025:::
Asmith:”":E165F0192EF85EBBAAD3B435B51404EE:E4EBE0E7EF708DC9FD240135D3D43D89:::
Bsmith:”":136A8418CF76C4F7AAD3B435B51404EE:3431E75AD08DCA56EB53AEAAB9926589:::
csmith:”":BB26C063532826AA531C3383FDDBFF2A:A2746ED4129985C0251D2B968C4889FE:::
Dsmith:”":A8EED815A197BD87AAD3B435B51404EE:F09A31889C35B8C9746B8F31FC3A868F:::
Esmith:”":5A9DB9F8BB5DF0CBAAD3B435B51404EE:5FCC20A69EC76AD91214102B4D7DE24E:::
Fsmith:”":213D466DB5B288F0F82E44EC0938F4F4:FAF10460760FA3F1ED804C7C724CB3D4:::
Gsmith:”":385A83A746BFA8F2AAD3B435B51404EE:1CC1B3958B564125D307BA8D9D60DF69:::
Hsmith:”":78BCCAEE08C90E29AAD3B435B51404EE:972E8E7D5568F70AC896B2C76E1395DC:::
Jsmith:”":59E2DB85E9D49595B75E0C8D76954A50:147D125645D463C33D72309525E9B0BC:::
Ksmith:”":59E2DB85E9D49595B75E0C8D76954A50:147D125645D463C33D72309525E9B0BC:::
Lsmith:”":13D855FC4841C7B1AAD3B435B51404EE:3DCEBC92C0ED8F52B1D759DD35CF3F0F:::
Msmith:”":D71808BF36F81510ADEE49688244F15A:45E8DA896575E2F5455B037FCC5AA51A:::
Nsmith:”":9C92FA4960AC2536AAD3B435B51404EE:C318744C4291EA46BC65082636CC9509:::
Osmith:”":1153C3961EE58C3BAAD3B435B51404EE:672532E8C0C490BD47254DAED1CDCB36:::
Psmith:”":4A01C0E45FCA767AAAD3B435B51404EE:39981702716E054CBE6840A3CFD60327:::
Qsmith:”":6842A19CC4C509E0AAD3B435B51404EE:9FDA95FD6FCEE9C2C998CB8010F61F16:::
Rsmith:”":BC472F3BF9A0A5F63832C92FC614B7D1:D2A80A79980CFA21CB58B7CB129E2CAD:::
Ssmith:”":09755C01D2789BD8AAD3B435B51404EE:62F740C2EA31E10B54DB64CE12E867A6:::
Tsmith:”":13D855FC4841C7B1AAD3B435B51404EE:3DCEBC92C0ED8F52B1D759DD35CF3F0F:::
Usmith:”":9E2204E2058AC9E9417EAF50CFAC29C3:476541DEC5CB507A795FC1E989C9D36F:::
Vsmith:”":7F9CD2D7C93421D3F9DE51FBDAA2F725:16FAABB24B95B82EFC50B074B7324517:::
Wsmith:”":AC814111DF804A7482EFD6B2A69511D6:15B194EB8D8F27761E32F76B001553A0:::
Xsmith:”":AAD3B435B51404EEAAD3B435B51404EE:2321504F2FA9437FBBA66EA1623407D3:::
Ysmith:”":D5662E6B23655BF74EC0DA4207C2DE66:75344B75B5A96614FE179C0188A9634A:::
Zsmith:”":9224FC255C58C50E42B35806901777E7:0C105C9F4326C3AC100C2A5B7A04AD38:::
The Answers so you can check your work.
testuser1 testuser1 (2)
remote password (2)
joeuser password (2)
averageguy average (1)
harderpass rootwars (2)
demouser demopass (2)
randy randy (1)
Asmith ABCd (1)
Bsmith ef456 (1)
csmith ABC789!@#12 (2)
Dsmith 3!@# (1)
Esmith 456!@# (1)
Fsmith ABCdef!@# (2)
Gsmith gHgHgH (1)
Hsmith ABC123 (1)
Jsmith ABCdef123^ (2)
|
Ksmith ABCdef123 (2)
Lsmith ABCdef (1)
Msmith FOOTBALL!@# (2)
Nsmith SOCCER (1)
Osmith CROKET (1)
Psmith COW123 (1)
Qsmith HOWNOW (1)
Rsmith BROWNCOW (2)
Ssmith gHaNdI (1)
Tsmith ABCdef (1)
Usmith RTdotnet (2)
Vsmith !pa55word! (2)
Wsmith EASYoneISNTit (2)
Xsmith C@NTcR8ckm3CanU? (X)no LM
Ysmith LSOISDABEST (2)
Zsmith RAINBOWTABLEZ (2)
|
**32 users and 47 LM hashes 48 Total hashes. Xsmith will only be saved as NTLM because it’s greater than 14 characters.
You should see something similar to the following:

Figure 1.1: Rcrack at work with an lm_alpha rainbow table

Figure 1.2: The results of our cracking attempt. 26 of our 41 hashes found in about 12 minutes. Also notice that the hash for the password “password” is the same because there is no salting with the LAN Manager hashing algorithm.
statistics
——————————————————-
plaintext found: 26 of 41 (63.41%)
total disk access time: 62.51 s
total cryptanalysis time: 742.77s
total chain walk step: 203410183
total false alarm: 195135
total chain walk step due to false alarm: 142852030
result
——————————————————-
testuser1 TESTUSE<notfound> hex:54455354555345<notfound>
remote password hex:70617373776f7264
joeuser password hex:70617373776f7264
averageguy average hex:61766572616765
harderpass rootwars hex:726f6f7477617273
demouser demopass hex:64656d6f70617373
randy randy hex:72616e6479
Asmith ABCd hex:41424364
Bsmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
csmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Dsmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Esmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Fsmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Gsmith gHgHgH hex:674867486748
Hsmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Jsmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Ksmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Lsmith ABCdef hex:414243646566
Msmith FOOTBAL<notfound> hex:464f4f5442414c<notfound>
Nsmith SOCCER hex:534f43434552
Osmith CROKET hex:43524f4b4554
Psmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Qsmith HOWNOW hex:484f574e4f57
Rsmith BROWNCOW hex:42524f574e434f57
Ssmith gHaNdI hex:6748614e6449
Tsmith ABCdef hex:414243646566
Usmith RTdotnet hex:5254646f746e6574
Vsmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Wsmith EASYoneISNTit hex:454153596f6e6549534e546974
Xsmith hex:
Ysmith LSOISDABEST hex:4c534f4953444142455354
Zsmith RAINBOWTABLEZ hex:5241494e424f575441424c455a
Example 2:
We are going to build our own tables using Configuration #1
**Note if you built your configuration #0 tables using rtgen use winrtgen (see exercise 4)
configuration #1
|
hash algorithm
|
lm
|
charset
|
alpha-numeric(ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789)
|
plaintext length range
|
1 – 7
|
key space
|
36^1 + 36^2 + 36^3 + 36^4 + 36^5 + 36^6 + 36^7 = 80603140212
|
t
|
2400
|
m
|
40000000
|
l
|
5
|
disk usage
|
m * 16 * l = 3200000000 B = 3 GB
|
success rate
|
0.9904
|
mean cryptanalysis time
|
7.6276 s
|
mean cryptanalysis time on a low memory system (free memory size much smaller than 610MB)
|
13.3075 s
|
max cryptanalysis time
|
40.6780 s
|
Table pre-computation commands:
rtgen lm alpha-numeric 1 7 0 2400 40000000 all
rtgen lm alpha-numeric 1 7 1 2400 40000000 all
rtgen lm alpha-numeric 1 7 2 2400 40000000 all
rtgen lm alpha-numeric 1 7 3 2400 40000000 all
rtgen lm alpha-numeric 1 7 4 2400 40000000 all
On a 666 MHz machine the table pre-computation time is about 15 days 17 hours, my P4 3.2 GHz with 1GB of RAM I created a table a day; so about 5 days.

Figure 2.1: Creating our LM alpha-numeric rainbow tables.
Now run that table against the same hash file, don’t forget to sort them first. You should crack most, if not all, of the alpha-numeric passwords, as opposed to alpha passwords only from configuration #0.

Figure 2.2: The results of our attempts. 32 of 41 passwords were found. Note that I ran this on my 3.2 GHz machine because I created the tables on it and didn’t want copy 3GB of rainbow tables to the slow computer.
statistics
——————————————————-
plaintext found: 32 of 41 (78.05%)
total disk access time: 233.84 s
total cryptanalysis time: 233.05 s
total chain walk step: 211003249
total false alarm: 104620
total chain walk step due to false alarm: 91734872
result
——————————————————-
testuser1 testuser1 hex:746573747573657231
remote password hex:70617373776f7264
joeuser password hex:70617373776f7264
averageguy average hex:61766572616765
harderpass rootwars hex:726f6f7477617273
demouser demopass hex:64656d6f70617373
randy randy hex:72616e6479
Asmith ABCd hex:41424364
Bsmith ef456 hex:6566343536
csmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Dsmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Esmith <notfound> hex:<notfound>
Fsmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Gsmith gHgHgH hex:674867486748
Hsmith ABC123 hex:414243313233
Jsmith ABCdef123 hex:414243646566313233
Ksmith ABCdef123 hex:414243646566313233
Lsmith ABCdef hex:414243646566
Msmith FOOTBAL<notfound> hex:464f4f5442414c<notfound>
Nsmith SOCCER hex:534f43434552
Osmith CROKET hex:43524f4b4554
Psmith COW123 hex:434f57313233
Qsmith HOWNOW hex:484f574e4f57
Rsmith BROWNCOW hex:42524f574e434f57
Ssmith gHaNdI hex:6748614e6449
Tsmith ABCdef hex:414243646566
Usmith RTdotnet hex:5254646f746e6574
Vsmith <notfound><notfound> hex:<notfound><notfound>
Wsmith EASYoneISNTit hex:454153596f6e6549534e546974
Xsmith hex:
Ysmith LSOISDABEST hex:4c534f4953444142455354
Zsmith RAINBOWTABLEZ hex:5241494e424f575441424c455a
Example 3:
Compare the results of the same hash file with Cain in Brute force mode, John the Ripper, and LC4.
Cain, in brute-force mode with an alpha-numeric character set, says it will take about 10 hours.

Figure 3.1: Cain in brute-force mode.

Figure 3.2: After 9+ hours it cracked 27 of the 41 hashes
John the Ripper, in default mode, was able to quickly (about 3 minutes) crack 32 of the 48 hashes.

Figure 3.3: JTR at work.
After 24 hours we had 45 of the 48 hashes.

Figure 3.4: JTR after 24 hours of cracking
The results of our efforts! All but 3 of the hashes were cracked in 24 hours by John. The “Xsmith” account with 15 characters was not cracked. With enough time we should have been able to find the passwords for “csmith” and “Vsmith”
Note that this really wasn’t a fair assessment since john will try characters not in our rainbow tables. If you want a really fair assessment, you should modify john’s ini file. But I don’t plan on doing it that. The point of the tables is the speed. But honestly, for this password file, John did really well.

Figure 3.5: the results 45 passwords cracked
Let’s see how LC4 fairs against our password file, I did turn off the dictionary and hybrid modes on LC4 and selected alphanumeric as our characters in the session options, so this should be a pretty fair “time to crack the same hashes” test.

Figure 3.6: Loading the password file of 32 users into LC4.

Figure 3.7: LC4 estimated about 11 hours to brute force crack the passwords using an alphanumeric character set.
In 11 hours we were able to crack 26 out of the 32 user accounts but the Xsmith account was not cracked because we did not attempt an NTLM attack.

Figure 3.8: So 11 hours versus 12.3795 minutes with the rainbow tables.
Example 4:
Using Cain and Abel’s Winrtgen to create your Rainbow Tables. Winrtgen supports Rainbow Tables for the following hashing/encryption algorithms: LM, FastLM, NTLM, CiscoPIX, MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA-1, SHA-2 (256), SHA-2 (384), SHA-2 (512), MySQL (323), MySQL (SHA1) and RIPEMD160.

Figure 4.1: Open Winrtgen and select Add Table

Figure 4.2: Select LM, 1 to 7 for Min/Max Length, Chain Length 2400 and Chain Count 40,000,000.
As you see with one table we get about 60% success rate and it will take about 2 days to create the table on a P3 1GHz machine. Feel free to manipulate Chain Length (remember that it will increase success rate but increase computation time) to whatever you can handle for table pre-computation time. I will leave it at 2400 for now. But 60% isn’t that great, for a 99.06% success rate you will need to create 5 tables (3 GB of space) and it will take about 12 days to create the tables. For a 99.63% success rate you will need to create 6 tables (3.57 GB of space) and it will take about 14 days to generate the tables. I will go with 5 tables for a success rate of 99.06%.

Figure 4.3: Creating 5 rainbow tables with a success rate of 99.06% using about 3 GB of space.
Here is a handy reference table:
There are some typical configurations (for LM hash type, length from 1 to 7) you can use, for example:
|
#1
|
#2
|
#3
|
#4
|
Charset
|
alpha
|
alpha-numeric
|
alpha-num-sym14
|
all
|
Chain length
|
2,100
|
2,400
|
12,000
|
20,000
|
Chain count
|
8,000,000
|
40,000,000
|
40,000,000
|
100,000,000
|
Tables
|
5
|
7
|
13
|
20
|
Success rate
|
99.9%
|
99.9%
|
99.9%
|
99,6%
|
Total space
|
640 Mb
|
4,480 Mb
|
8,320 Mb
|
32,000 Mb
|
Max gen. time
|
18h 35m
|
6d 5h
|
67d 18h
|
369d
|
Max analysis time
|
8 s
|
16 s
|
15 m
|
53 m
|
Example 5:
Using Cain and Abel to crack passwords using Rainbow Tables
Step 1: Download [8] and install Cain.
Step 2: Click on the “Cracker” tab. Select what type of passwords you want to crack. In this case LM & NTLM Hashes. Then right click and select “add to list.” Navigate to where you have your text file of hashes, select it and then select next.

Figure 5.1: Loading hashes from file

Figure 5.2: Hashes loaded into Cain, ready to be cracked.
Step 3: Right click and select “select all” then right click again and select cryptanalysis attack and “LM Hashes via Rainbow Tables”

Figure 5.3: Selecting a cryptanalysis attack via Rainbow Tables.
Step 4: Click on Add Table. Then navigate to where you have your rainbow tables, highlight them all and select Open.

Figure 5.4: Adding your rainbow tables to use for cracking.
Step 5: Click on “Start” and Cain will start to work through the rainbow tables.

Figure 5.5: Cain working through the Rainbow Tables cracking passwords.
Step 6: When its all done click Exit and it will show you the cracked passwords.

Figure 5.6: Cain finishes running though the Rainbow Tables.

Figure 5.7: Our cracked passwords in Cain. Notice that Cain also found the NTLM password based on the LM password.
I am still confused what does “X, Y, or Z” mean?
Here are some things that may not be immediately clear when dealing with rainbow tables:
1- What do “t”, “m”, and “l” mean or stand for?
To answer this, let’s analyze an rtgen command:
rtgen lm alpha 1 7 0 2100 8000000 all
rtgen obviously means the program to run. “lm” means we want to generate LAN Manager tables. “alpha” mean we want to use the characters listed in our charset.txt file for alpha:
alpha = [ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ]
“1” and “7” are our plaintext ranges. So we want passwords from “A” to “ZZZZZZZ.” If we had put plaintext length range “4-6″, “AAAA” and “ZZZZZZ” would be among the key space; but “AAA” would not because it has a length 3. Remember that, for LAN Manager , passwords they are broken up into 7 character chunks, so there would be no need to do a plaintext range of 1 to 8. The “0” is our table number or rainbow table count, if you look at the rtgen commands to generate configuration #0 we create five tables 0 to 4. This is so we can split up tables between computers making the rainbow tables and to increase our success rate. “2100” is our rainbow chain length. Chain length increases the success rate per table but does not increase table size. It computes more hashes per chain but also takes longer to create and search the table. A common “upper” value for chain length is 4000-5000. “8000000” is our rainbow chain count of each rainbow table. Chain count is simply how many chains you want per table. Increasing this value produces larger files with higher success rates, but the overall computation time isn’t affected. You can adjust the chain count so your rainbow tables are conveniently sized (like for a CD or DVD). The “all” is our file title suffix or what we want appended to the end of our table’s file name, it can be anything you want.
2- What do the different chain lengths and chain counts mean?
Chain Length increases the success rate per table. It computes more hashes per chain but also takes longer to create and search the table. A common “upper” value for chain length is 4000-5000 but it can be whatever you want. Chain count is simply how many chains you want per table. Increasing this value produces larger files with higher success rates, but the overall computation time isn’t affected. You can adjust the chain count so your rainbow tables are conveniently sized (like for a CD or DVD) or to increase the success rate.
3- Why can’t I create just one rainbow table?
You can! But to get a high enough success rate that table will be too large to search in a reasonable amount of time. That is why we normally create several. Now we could, by adjusting chain length and chain count, create a giant rainbow table but we will have to sort it, which will take a long time and then search it, which will take an even longer time; thus reducing the whole point of rainbow tables. It would be a more efficient use of space to create many rainbow tables so you can sort and search them faster.
4-I am still confused!
Then 1) go read the paper: http://lasecwww.epfl.ch/php_code/publications/search.php?ref=Oech03 and 2) check out the next section for some examples with Winrtgen which allows you to see (graphically) how changing values changes success rates, table size, and table generation time.
Using Winrtgen to see how chain length, chain count and number of tables effects success rate and computation time
We can see in this example that we get a 97.80% success rate with one LM ALPHA rainbow table with a Chain Length of 2400 and a Chain Count of 40,000,000. It will take 2.23 days to generate the table on the computer (a P3 1.0 Ghz with 512 MB of RAM).

Increasing the Chain Length to 4000 increases our success rate to 99.11% but it now takes 3.67 days to generate the table.

LM Configuration #0 Configuration with 1 table. 75% success rate but only takes 9 hours to generate the table.

LM Configuration #0 with 5 tables (the recommended configuration). Notice that for roughly the same amount of time and space as our first example with a Chain Length of 2400 and a Chain Count of 40,000,000 and a success rate of 97.80% we can get 99.90% with this Rainbow Table configuration. Another thing to note that we don’t see is sort time and how much longer it takes to sort one big table versus several smaller tables.

Let’s see how long it takes to create tables to find “all” possible password combinations—minus “ALT-XXX commands.” For a 1GB table it will take 23 days with a 12.25% success rate.

And it will take 4.6 years (on a P3 1GHz machine) to generate enough tables to reach 99.98%!!!

Protecting yourself against RainbowCrack attacks and other password attacks
-Limiting physical access
-Continue to force the use of special characters
-Use ALT-XXX characters in your passwords
-Keep up with updates
-Use Pass phrases
-Use Multi-factor authentication
-Password Policy
-Use NTLM or NTLMv2
What if my Windows password is longer than 14 characters or the LAN Manager hash is not stored?
If your systems do not require the LAN Manager (LM) hash (for example if you are running an Active Directory (AD) domain), or if your password is >14 characters long, the LM hash will be stored as the blank LM hash, even though the clear text password itself is not blank. Basically none of the cracking tools will see a LM hash.
If this is the case, you will need to audit your password hashes against the NTLM character set.
Limiting physical access
It’s a well-known fact that if someone has physical access to a machine then it’s not secure. They can walk off with it, take the hard drive, turn it off, etc. One common attack if you have physical access to a machine is to use a bootable Linux distro to simply boot into Linux and grab the SAM file off the windows partition. You can then crack it at your leisure. IronGeek wrote a good tutorial on this method and even has a video you can watch. You can get it here: http://www.irongeek.com/i.php?page=security/localsamcrack2. Another interesting tool released by Eeye is SysRQ2: http://research.eeye.com/html/tools/RT20060801-8.html. “SysRq is a bootable CD image that allows a user to open a fully privileged (SYSTEM) command prompt on Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 systems by pressing Ctrl+Shift+SysRq at any time after startup.”
Continue to force the use of special characters
Even though rainbow tables can rip thru a LM password with any type of special character it still takes a large amount of time (1-2 years) to generate them, this will deter most people or force them to use an online hash cracking service [9]. It also greatly increases the time for brute force attempts. In LC4 we go from 9-11 hours to brute force alpha-numeric password to 91 days to brute force passwords with the possibility of all special characters (minus ALT-XXX passwords).

Brute-force cracking time is greatly increased by using special characters in your passwords. From 9 hours with just alpha-numeric to 91 days with all characters.
Use ALT-XXX characters in your passwords
ALT characters are produced by holding down the ALT key (or FN-ALT keys on some laptops) and pressing a three or four digit number sequence on your keypad. Most password crackers cannot crack passwords with ALT characters. Most ALT characters also have the added benefit that passwords that have ALT characters in them cannot be stored as LM hashes.
ALT characters which cause the LMHash to disappear
0128-0159
|
0306-0307
|
312
|
0319-0320
|
0329-0331
|
383
|
0385-0406
|
0408-0409
|
0411-0414
|
0418-0424
|
426
|
0428-0429
|
0433-0437
|
0439-0447
|
0449-0450
|
0452-0460
|
477
|
0480-0483
|
0494-0495
|
0497-0608
|
0610-0631
|
0633-0696
|
699
|
0701-0707
|
709
|
711
|
716
|
0718-0729
|
731
|
0733-0767
|
0773-0775
|
777
|
0779-0781
|
0783-0806
|
0808-0816
|
0819-0893
|
0895-0912
|
914
|
0918-0919
|
0921-0927
|
0929-0930
|
933
|
0935-0936
|
0938-0944
|
947
|
0950-0955
|
0957-0959
|
0961-0962
|
965
|
0967-1024
|
|
|
Some ALT characters not listed above, firstly, can still be stored as LM Hashes and secondly, can weaken your password because they are converted to uppercase before they are stored. If you are going to use ALT characters go with the “safe” ones above.
A final note to add about ALT characters is that you may be unable to login to mixed environments with ALT passwords or be unable to authenticate to file shares using SAMBA or other non-Windows tools.
Keep up with updates
Keep up with your security patches. While you can’t protect against zero day exploits you can protect against exploits that have patches! All of the password dumping tools must have administrative level privileges to dump the hashes. You can keep the majority of the bad guys out by patching your machines promptly against public exploits. This will help keep you protected from that system/administrative level exploit that was just released to the public.
Use Pass phrases
Using pass phrases is the easiest and simplest way to protect you network from password cracking. If your password policy makes use of pass phrases that are greater than 14 characters AND use special characters you can protect yourself from all but the determined attackers. If your network is Windows 2000 and above you have a maximum length of 127 characters on your password/pass phrase; so sky’s the limit. A pass phrase like “This is my Stupid Pass Phrase!” is long enough to be stored as NTLM or NTLMv2 (because it is longer than 14 characters), has Uppercase, Lowercase, Spaces, and Special Characters, and is easy to remember. This is a much more secure password than even “@w3cjd$Beu=mDr”. If you can get your users to do some character substitution on their pass phrases even better!
The use of strong passwords within an environment needs to be mandated for users. Using the stronger NTLMv2 hashing scheme won’t prevent a successful dictionary attack. The use of strong passwords can be enforced on Windows NT through the use of the passfilt.dll. This is described in Microsoft Knowledgebase Article 161990 [10]. The use of strong passwords in Windows 2000, XP and 2003 can be enforced by settings in the Group Policy, which is described in Microsoft Knowledgebase Article 225230 [11].
Use Multi-factor authentication
Any decent CISSP could talk at length about multi-factor authentication and many have, so I won’t cover it much here except to say that any type of multi-factor authentication you can implement will help your network. Whether it be biometric, smartcard, token, etc, anything that makes a user need to provide more than a simple password to log on to your network helps your security posture and stops a cracked password in its tracks.
Password Policy
A strong password policy will:
- Insist on frequent password changes (frequency depends on the sensitivity of your data anywhere between 30-180 days)
- Require long passwords composed of random combinations of upper and lowercase letters, numbers and special characters
- Not allow blank passwords
- Check to ensure passwords are not repeated
- Prevent the use of any part of the user’s name or user ID
- Not allow the use of common dictionary words
On Windows 2000 or above with Active Directory, password management is fairly easily controlled and implemented using group policy. Forcing users to meet your password policy requirements is fairly easy with Active Directory and should be utilized if possible.
Use NTLM or NTLMv2
Instead of storing your user account password in clear-text, Windows generates and stores user account passwords by using two different password representations, generally known as “hashes.” When you set or change the password for a user account to a password that contains fewer than 15 characters, Windows generates both a LAN Manager hash (LM hash) and a Windows NT hash (NT hash) of the password. These hashes are stored in the local Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database or in Active Directory.
The LM hash is relatively weak compared to the NT hash, and it is therefore prone to fast brute force attack. Therefore, you may want to prevent Windows from storing an LM hash of your password
Windows 2000-based servers and Windows Server 2003-based servers can authenticate users who connect from computers that are running all earlier versions of Windows. However, versions of Windows earlier than Windows 2000 do not use Kerberos for authentication. For backward compatibility, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 support LAN Manager (LM) authentication, Windows NT (NTLM) authentication, and NTLM version 2 (NTLMv2) authentications. The NTLM, NTLMv2, and Kerberos all use the NT hash, also known as the Unicode hash. The LM authentication protocol uses the LM hash. The use of LAN Manager hashes on the network can be disabled on Windows NT, 2000, 2003 & XP through registry edits or through the Local Security Policy. The instructions to do so can be found at in Microsoft Knowledgebase Article 147706 [12]. The storage of LAN Manager hashes also needs to be disabled; this can be done for Windows 2000, XP and 2003 again via registry edits or the Local Security Policy. The instructions to do so can be found at in Microsoft Knowledgebase Article 299656 [13].
Method 1: Implement the NoLMHash Policy by Using Group Policy
To disable the storage of LM hashes of a user’s passwords in the local computer’s SAM database by using Local Group Policy (Windows XP or Windows Server 2003) or in a Windows Server 2003 Active Directory environment by using Group Policy in Active Directory (Windows Server 2003), follow these steps:
1.
|
In Group Policy, expand Computer Configuration, expand Windows Settings, expand Security Settings, expand Local Policies, and then click Security Options.
|
2.
|
In the list of available policies, double-click Network security: Do not store LAN Manager hash value on next password change.
|
3.
|
Click Enabled, and then click OK.
|
Method 2: Implement the NoLMHash Policy by Editing the Registry
Windows 2000 SP2 and Later
To add this key by using Registry Editor, follow these steps:
1.
|
Start Registry Editor (Regedt32.exe).
|
2.
|
Locate and then click the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa
|
3.
|
On the Edit menu, click Add Key, type NoLMHash, and then press ENTER.
|
4.
|
Quit Registry Editor.
|
5.
|
Restart the computer, and then change your password to make the setting active.
|
Notes
•
|
This registry key change must be made on all Windows 2000 domain controllers to disable the storage of LM hashes of users’ passwords in a Windows 2000 Active Directory environment.
|
•
|
This registry key prevents new LM hashes from being created on Windows 2000-based computers, but it does not clear the history of previous LM hashes that are stored. Existing LM hashes that are stored will be removed as you change passwords.
|
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003
1.
|
Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
|
2.
|
Locate and then click the following key in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa
|
3.
|
On the Edit menu, point to New, and then click DWORD Value.
|
4.
|
Type NoLMHash, and then press ENTER.
|
5.
|
On the Edit menu, click Modify.
|
6.
|
Type 1, and then click OK.
|
7.
|
Restart your computer, and then change your password.
|
Notes
•
|
This registry change must be made on all Windows Server 2003 domain controllers to disable the storage of LM hashes of users’ passwords in a Windows 2003 Active Directory environment. If you are a domain administrator, you can use Active Directory Users and Computers Microsoft Management Console (MMC) to deploy this policy to all domain controllers or all computers on the domain as described in Method 1 (Implement the NoLMHash Policy by Using Group Policy).
|
•
|
This DWORD value prevents new LM hashes from being created on Windows XP-based computers and Windows Server 2003-based computers. The history of all previous LM hashes is cleared when you complete these steps.
|
Windows NT
Control of NTLM security is through the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\control\LSA
Name: LMCompatibilityLevel
Type: REG_DWORD
Value: 5 : DC refuses LM and NTLM responses (accepts only NTLMv2)
Value: 4 : DC refuses LM responses
Value: 3 : Send NTLMv2 response only
Value: 2 : Send NTLM response only
Value: 1 : Use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated
Value: 0 : default – Send LM response and NTLM response; never use NTLMv2 session security
More information on the values:
Level 0 – Send LM and NTLM response; never use NTLM 2 session security. Clients use LM and NTLM authentication, and never use NTLM 2 session security; domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLM 2 authentication.
Level 1 – Use NTLM 2 session security if negotiated. Clients use LM and NTLM authentication, and use NTLM 2 session security if the server supports it; domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLM 2 authentication.
Level 2 – Send NTLM response only. Clients use only NTLM authentication, and use NTLM 2 session security if the server supports it; domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLM 2 authentication.
Level 3 – Send NTLM 2 response only. Clients use NTLM 2 authentication, and use NTLM 2 session security if the server supports it; domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLM 2 authentication.
Level 4 – Domain controllers refuse LM responses. Clients use NTLM authentication, and use NTLM 2 session security if the server supports it; domain controllers refuse LM authentication (that is, they accept NTLM and NTLM 2).
Level 5 – Domain controllers refuse LM and NTLM responses (accept only NTLM 2). Clients use NTLM 2 authentication, use NTLM 2 session security if the server supports it; domain controllers refuse NTLM and LM authentication (they accept only NTLM 2).
Method 3: Use a Password That Is at Least 15 Characters Long
The simplest way to prevent Windows from storing an LM hash of your password is to use a password that is at least 15 characters long. In this case, Windows stores an LM hash value that cannot be used to authenticate the user.
To get an idea of the power of using NTLM for your hash algorithm lets see how long it will take to generate a NTLM mixed-alphanumeric rainbow table with Winrtgen:

For a mixed-alphanumeric NTLM table it will take 2.5 days to generate one table with a 4.32% success rate.

It will take over 100 rainbow tables, 60 GB of space, and 252 days to create the tables to crack the same passwords (with a 98.80% success rate) we have been attacking throughout this paper if they were stored as NTLM instead of LM!
Conclusion
As you can see Rainbow Tables and RainbowCrack are powerful password auditing tools. The best course of action to protect yourself is to not allow the storage and use of LAN Manager (LM) passwords on your network if you don’t absolutely need to and to create and enforce a strong password policy that will force the storage and use of passwords as NTLM and not LM. Additionally, the time to compute and space requirements of complex Rainbow Tables should limit the use of them to only determined attackers or auditors. A strong password policy, strong domain security policy, and keeping up with your patches and updates are your best safeguards against password attacks.
References
RainbowCrack–Not a New Street Drug
http://redmondmag.com/columns/article.asp?EditorialsID=736
Rainbow Tables: Nature, Use, and Generation
http://security.the-engine.org/documents/48/rainbow-tables-nature-use-and-generation
“Faster Cryptanalytic time – memory trade off’ paper by Philippe Oechslin
http://lasecwww.epfl.ch/php_code/publications/search.php?ref=Oech03
Project RainbowCrack
http://www.antsight.com/zsl/rainbowcrack/
Get Free Rainbow Tables via torrent files
http://rainbowtables.shmoo.com/
The Tactical Use of RainbowCrack to Exploit Windows Authentication in a Hybrid Physical-Electronic Attack by Mike Mahurin
http://www.giac.org/practicals/GCIH/Mike_Mahurin_GCIH.pdf
Password Cracking: Rainbow Tables Explained
https://www.isc2.org/cgi-bin/content.cgi?page=738
How to prevent Windows from storing a LAN manager hash of your password in Active Directory and local SAM databases
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=KB;EN-US;q299656&
How to disable LM authentication on Windows NT
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q147706
How to enable NTLM 2 authentication
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q239869
Microsoft Windows 2000 Security Hardening Guide
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/prodtech/windows2000/win2khg/03osinstl.mspx
10 tips in 10 minutes: Password policy considerations
http://searchwindowssecurity.techtarget.com/originalContent/0,289142,sid45_gci1044698,00.html
For use of useradd.txt to create the users:
http://www.rainbowtables.net
About the Author
Chris Gates, CISSP serves as the operations manager and course mentor for LearnSecurityOnline.com. Feel free to email comments and suggestions on the tutorial to chris [at] learnsecurityonline [dot] com.
Footnotes
[1] http://lasecwww.epfl.ch/php_code/publications/search.php?ref=Oech03
[2] http://securitynews.weburb.org/show.php3?item=newsboard&p%5BmessageId%5D=3090
[3] http://lasecwww.epfl.ch/philippe.shtml
[4] http://lasecwww.epfl.ch/~oechslin/publications/crypto03.pdf
[5] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rainbow_table
Free Template Blogger
collection template
Hot Deals
SEO














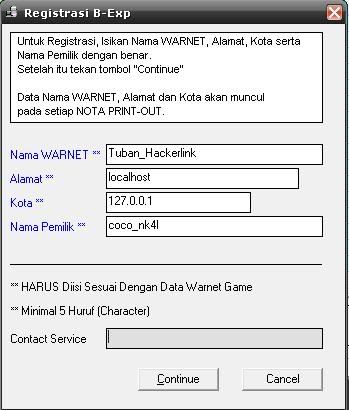
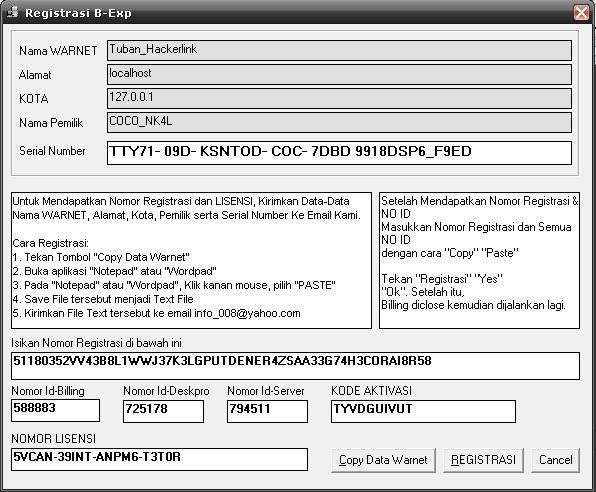
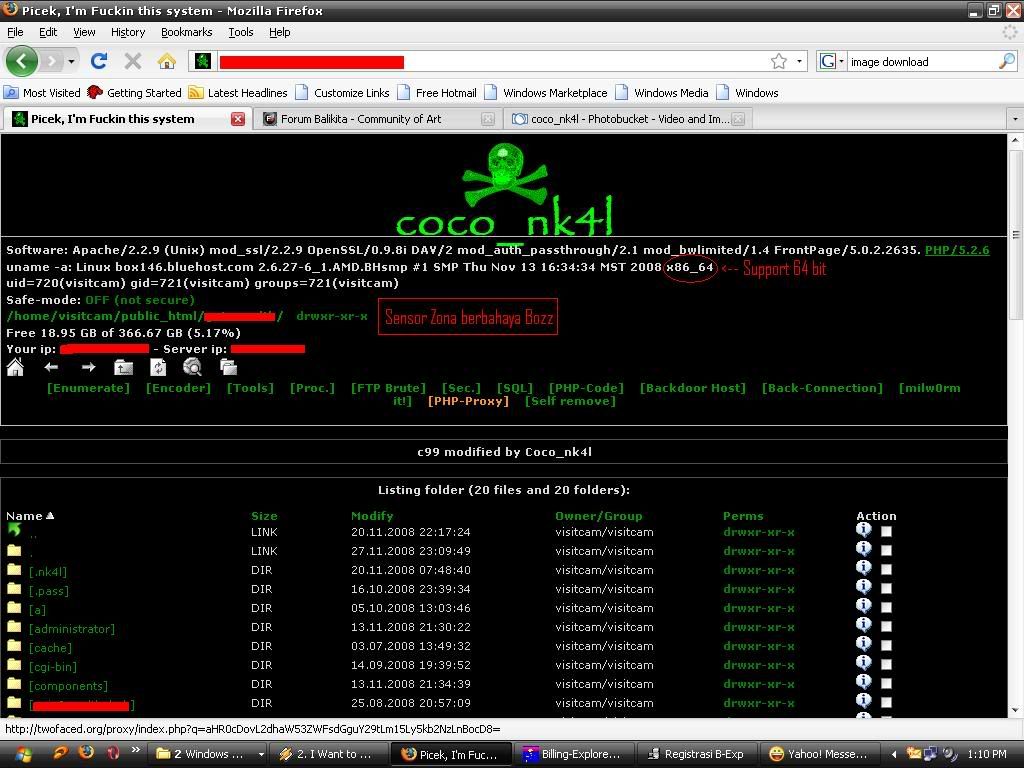
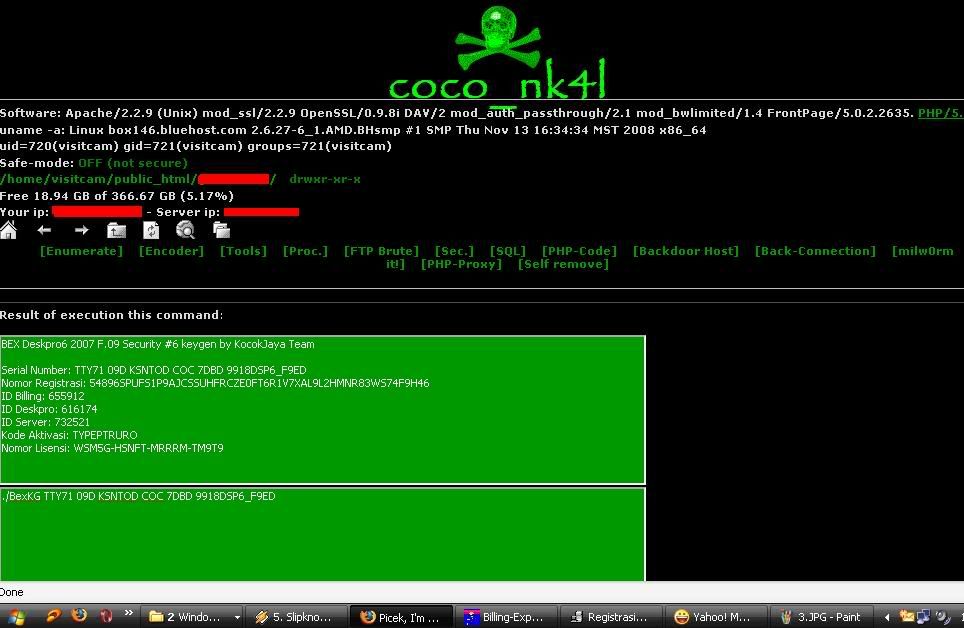
 Test registrasi kalo ada Peringatan Kode Registrasi sudah benar berarti mang dah Finish....
Test registrasi kalo ada Peringatan Kode Registrasi sudah benar berarti mang dah Finish.... pakabar sob dekaters ?? gimana da pahamin lom posting sebelumnya?? pasti rada puyeng ya!! ato malah pusingnya ampe sekarang belom sembuh ? hehhehe, kali ini kita tambahin pusing kalian jadi 2 ( dua ) kali lipat ato bahkan berlipat-lipat
pakabar sob dekaters ?? gimana da pahamin lom posting sebelumnya?? pasti rada puyeng ya!! ato malah pusingnya ampe sekarang belom sembuh ? hehhehe, kali ini kita tambahin pusing kalian jadi 2 ( dua ) kali lipat ato bahkan berlipat-lipat  ) Ok Sob , kita langusng ke pokok pembahasan tapi pesan kita
) Ok Sob , kita langusng ke pokok pembahasan tapi pesan kita 










































